Appboard/2.4/builder/widgets/circular gauge: Difference between revisions
imported>Mike.berman (create page for AppBoard 2.4) |
imported>David.moore m (→Data Step) |
||
| (23 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{DISPLAYTITLE:Circular Gauge Widget}} | |||
[[Category:AppBoard 2.4]] | |||
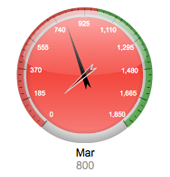
[[File:CircularGaugeExample.png|frame|center||Circular Gauge Sample]] | |||
== Sample Data == | == Sample Data == | ||
Instructions for bringing sample chart data into AppBoard can be found here: [[ | Instructions for bringing sample chart data into AppBoard can be found here: [[appboard/2.4/builder/sample_chart_data|Sample Chart Data]] | ||
== Adding a Circular Gauge Widget == | == Adding a Circular Gauge Widget == | ||
=== Data Step === | |||
# add a widget by clicking the ''Add Widget'' quick action on the left, or via the ''Widgets'' page. | |||
# On the ''Widget Type'' selection choose the ''Circular Gauge'' by first navigating to the ''Gauge'' category. | |||
# Set the ''Data Collection'' | |||
# Set the ''Widget Name'' | |||
# continue onto the ''Visualization'' step. | |||
{{Tip|If using the sample data the most appropriate data collection is <tt>Sample.Data.ChartData</tt>.}} | |||
== | === Visualization Step === | ||
==== Label Field==== | |||
== Label Field== | |||
Select a field that contains the desired label to be used for each item in the data set. | Select a field that contains the desired label to be used for each item in the data set. | ||
* The "rows" of data from this field (column) will be used as the label for each gauge. | * The "rows" of data from this field (column) will be used as the label for each gauge. | ||
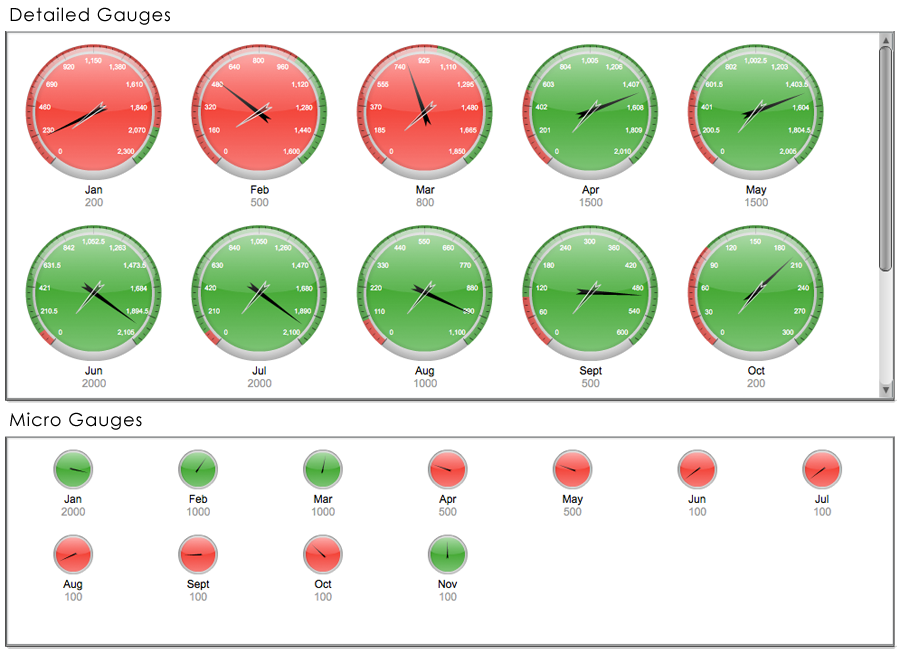
If you are using ''Sample.Data.ChartData'', select "Month" to be the Label Field. This will produce 11 gauges, since there are 11 rows of data in the sample file. Each will have a different Month name as their label. | |||
== Second Label Field == | ==== Second Label Field ==== | ||
Select a field that contains the desired secondary label to be used for each item in the data set. | Select a field that contains the desired secondary label to be used for each item in the data set. | ||
* The "rows" of data from this field (column) will be used as the secondary label for each gauge. directly below the Label Field, beneath the gauge. | * The "rows" of data from this field (column) will be used as the secondary label for each gauge. directly below the Label Field, beneath the gauge. | ||
If you are using ''Sample.Data.ChartData'', select "Planning" to be the Label Field. This will produce 11 gauges, since there are 11 rows of data in the sample file. Each will have a different Month name as their label. | |||
==== Value Field ==== | |||
The "Value Field" is what determines the placement of the needle inside the Gauge component. | The "Value Field" is what determines the placement of the needle inside the Gauge component. | ||
If you're using ''Sample.Data.ChartData'', select "Software" as the Value Field. | |||
==== Thresholds (Color) ==== | |||
Setting thresholds is an important element in configuring the Gauge Widget. Threshold values determine the colors displayed in the gauge, as well as the numeric labels that are displayed around the gauge. | |||
# '''Dynamic''': Select one or more fields in the <b>Value</b> column, and AppBoard will derive threshold values from the data that is currently displayed in the Widget. This is useful if the values being plotted are compared against different scales. | |||
## Determining Thresholds: A consistent "Max" value is used across all the gauges, using a "Max Value" option in the Threshold pull-down | |||
## Examples of threshold usages: | |||
##* Projected vs. Actual: Shows the variation in projections by region as well as the actual values for that region. | |||
##* SLA: Shows variation between service level agreements per customer as well as the actual SLA values. | |||
# '''Dynamic''': Select one or more fields in the <b>Value</b> column, and AppBoard will derive threshold values from the data that is currently displayed in the Widget. This is useful if the values being plotted are compared against different scales. | |||
#* Projected vs. Actual: Shows the variation in projections by region as well as the actual values for that region. | |||
#* SLA: Shows variation between service level agreements per customer as well as the actual SLA values. | |||
# '''Static''': Lets you manually enter a static threshold value(s) to use across the data set. AppBoard will find the highest value of all the entered "Static" <b>Value</b> fields, and then automatically determine the 10 breakpoints to display, based on interpolating between (a) the greater of the lowest data value or "Start Value", and (b) the highest data value. The coloration of the gauge will also be determined by comparing the <b>Value Field</b> against the "Static" <b>Value</b> fields. | # '''Static''': Lets you manually enter a static threshold value(s) to use across the data set. AppBoard will find the highest value of all the entered "Static" <b>Value</b> fields, and then automatically determine the 10 breakpoints to display, based on interpolating between (a) the greater of the lowest data value or "Start Value", and (b) the highest data value. The coloration of the gauge will also be determined by comparing the <b>Value Field</b> against the "Static" <b>Value</b> fields. | ||
#* Tickets: If there are more than 50 active tickets for any given location, the gauge background should turn red. Create a single Threshold, entering "50" for the "Static" value and select the red color. | #* Tickets: If there are more than 50 active tickets for any given location, the gauge background should turn red. Create a single Threshold, entering "50" for the "Static" value and select the red color. | ||
#* Events: When total number of critical events for a system exceeds 10, the gauge background should turn red (if "Tint Gauge with Threshold Color" option is selected). | #* Events: When total number of critical events for a system exceeds 10, the gauge background should turn red (if "Tint Gauge with Threshold Color" option is selected). | ||
# '''Derived''': Select one of: | |||
#* ''Min Value'': Will use the minimum value found (in the column selected by the 'Value Field' parameter) as a threshold. | |||
#* ''Avg Value'': Will use the average value found (in the column selected by the 'Value Field' parameter) as a threshold. | |||
#* ''Max Value'': Will use the maximum value found (in the column selected by the 'Value Field' parameter) as a threshold. | |||
If you are using ''Sample.Data.ChartData'', then set Red to "Dynamic" "Hardware", and Green to "Dynamic" "Totals". | |||
Note that the order specified is significant. The thresholds should be specified in greatest magnitude to least or from least to greatest. Notice that '0' is always an implied threshold unless overridden by 'Start Value' in 'Presentation', and will be specified last in the greatest to least scenario or first in the least to greatest scenario. For instance, the specified thresholds (10,20,30) will result in the ranges (0-10,10-20,20-30). The thresholds (30,20,10) will result in the ranges (30-20,20-10,10-0). | |||
=== Presentation Step === | |||
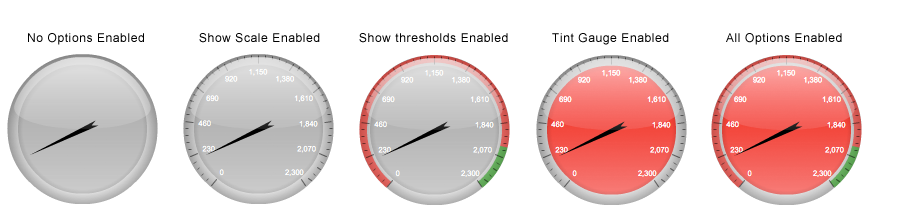
== Gauge Options == | ==== Gauge Options ==== | ||
The gauge widget has several unique rendering options. | The gauge widget has several unique rendering options. | ||
* '''Show Scale in Gauge''': This option shows numerical labels inside the gauge. | * '''Show Scale in Gauge''': This option shows numerical labels inside the gauge. | ||
* '''Show Thresholds in Gauge''': This option shows threshold colors on the outside edge of the gauge when enabled. | * '''Show Thresholds in Gauge''': This option shows threshold colors on the outside edge of the gauge when enabled. | ||
* '''Tint Gauge with Threshold Color''': This option will tint the face of the gauge with the appropriate threshold color when enabled. | * '''Tint Gauge with Threshold Color''': This option will tint the face of the gauge with the appropriate threshold color when enabled. | ||
[[Image:Gauge_Options.png|Gauge Options]] | [[Image:Gauge_Options.png|750px|Gauge Options]] | ||
* '''Comparitive Measure Field''': See section above. | * '''Comparitive Measure Field''': See section above. | ||
==== Gauge Size ==== | |||
The Gauge Size slider affects how large the gauges are, which will impact the number of gauges that can be displayed in a particular Widget. | The Gauge Size slider affects how large the gauges are, which will impact the number of gauges that can be displayed in a particular Widget. | ||
[[Image:Gauge_Sizes.png|Gauge Sizes]] | [[Image:Gauge_Sizes.png|750px|Gauge Sizes]] | ||
==== Start Value ==== | |||
This option will crop the range of values used to determine the rotation of the needle. This option is useful when dealing with values that do not have much variation. For Example, SLA calculations usually result in values clustered around 99%. If you start from zero, then the gauge will show nearly identical needles. With a "Start Value" set at .095, the needles will show more variation, providing a more useful comparison across the data set as a whole. | |||
==== Comparative Measure ==== | |||
Comparative Measure is an optional secondary (shorter) needle that can be shown on each gauge. It can be useful for showing a high water mark, or deviations from an historical average. | |||
* Select a field that contains the desired value to use in placing the needle to show the comparative measure. | |||
== Additional Configuration Steps == | == Additional Configuration Steps == | ||
* See the following page for detail on configuring Widget Options: [[ | * See the following page for detail on configuring Widget Options: [[appboard/2.4/builder/widgets/options|Options]] | ||
* See the following page for detail on configuring Widget Actions: [[ | * See the following page for detail on configuring Widget Actions: [[appboard/2.4/builder/widgets/actions|Actions]] | ||
Latest revision as of 23:43, 24 December 2013
Sample Data
Instructions for bringing sample chart data into AppBoard can be found here: Sample Chart Data
Adding a Circular Gauge Widget
Data Step
- add a widget by clicking the Add Widget quick action on the left, or via the Widgets page.
- On the Widget Type selection choose the Circular Gauge by first navigating to the Gauge category.
- Set the Data Collection
- Set the Widget Name
- continue onto the Visualization step.
Visualization Step
Label Field
Select a field that contains the desired label to be used for each item in the data set.
- The "rows" of data from this field (column) will be used as the label for each gauge.
If you are using Sample.Data.ChartData, select "Month" to be the Label Field. This will produce 11 gauges, since there are 11 rows of data in the sample file. Each will have a different Month name as their label.
Second Label Field
Select a field that contains the desired secondary label to be used for each item in the data set.
- The "rows" of data from this field (column) will be used as the secondary label for each gauge. directly below the Label Field, beneath the gauge.
If you are using Sample.Data.ChartData, select "Planning" to be the Label Field. This will produce 11 gauges, since there are 11 rows of data in the sample file. Each will have a different Month name as their label.
Value Field
The "Value Field" is what determines the placement of the needle inside the Gauge component.
If you're using Sample.Data.ChartData, select "Software" as the Value Field.
Thresholds (Color)
Setting thresholds is an important element in configuring the Gauge Widget. Threshold values determine the colors displayed in the gauge, as well as the numeric labels that are displayed around the gauge.
- Dynamic: Select one or more fields in the Value column, and AppBoard will derive threshold values from the data that is currently displayed in the Widget. This is useful if the values being plotted are compared against different scales.
- Determining Thresholds: A consistent "Max" value is used across all the gauges, using a "Max Value" option in the Threshold pull-down
- Examples of threshold usages:
- Projected vs. Actual: Shows the variation in projections by region as well as the actual values for that region.
- SLA: Shows variation between service level agreements per customer as well as the actual SLA values.
- Static: Lets you manually enter a static threshold value(s) to use across the data set. AppBoard will find the highest value of all the entered "Static" Value fields, and then automatically determine the 10 breakpoints to display, based on interpolating between (a) the greater of the lowest data value or "Start Value", and (b) the highest data value. The coloration of the gauge will also be determined by comparing the Value Field against the "Static" Value fields.
- Tickets: If there are more than 50 active tickets for any given location, the gauge background should turn red. Create a single Threshold, entering "50" for the "Static" value and select the red color.
- Events: When total number of critical events for a system exceeds 10, the gauge background should turn red (if "Tint Gauge with Threshold Color" option is selected).
- Derived: Select one of:
- Min Value: Will use the minimum value found (in the column selected by the 'Value Field' parameter) as a threshold.
- Avg Value: Will use the average value found (in the column selected by the 'Value Field' parameter) as a threshold.
- Max Value: Will use the maximum value found (in the column selected by the 'Value Field' parameter) as a threshold.
If you are using Sample.Data.ChartData, then set Red to "Dynamic" "Hardware", and Green to "Dynamic" "Totals".
Note that the order specified is significant. The thresholds should be specified in greatest magnitude to least or from least to greatest. Notice that '0' is always an implied threshold unless overridden by 'Start Value' in 'Presentation', and will be specified last in the greatest to least scenario or first in the least to greatest scenario. For instance, the specified thresholds (10,20,30) will result in the ranges (0-10,10-20,20-30). The thresholds (30,20,10) will result in the ranges (30-20,20-10,10-0).
Presentation Step
Gauge Options
The gauge widget has several unique rendering options.
- Show Scale in Gauge: This option shows numerical labels inside the gauge.
- Show Thresholds in Gauge: This option shows threshold colors on the outside edge of the gauge when enabled.
- Tint Gauge with Threshold Color: This option will tint the face of the gauge with the appropriate threshold color when enabled.
- Comparitive Measure Field: See section above.
Gauge Size
The Gauge Size slider affects how large the gauges are, which will impact the number of gauges that can be displayed in a particular Widget.
Start Value
This option will crop the range of values used to determine the rotation of the needle. This option is useful when dealing with values that do not have much variation. For Example, SLA calculations usually result in values clustered around 99%. If you start from zero, then the gauge will show nearly identical needles. With a "Start Value" set at .095, the needles will show more variation, providing a more useful comparison across the data set as a whole.
Comparative Measure
Comparative Measure is an optional secondary (shorter) needle that can be shown on each gauge. It can be useful for showing a high water mark, or deviations from an historical average.
- Select a field that contains the desired value to use in placing the needle to show the comparative measure.