Appboard/2.4/builder/system administration/session variables: Difference between revisions
imported>Jason.nicholls No edit summary |
imported>Jason.nicholls No edit summary |
||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
* Session Variables administration page to define and set defaults | * Session Variables administration page to define and set defaults | ||
* URL parameters to override session variables (only allowed if configured this way) | * URL parameters to override session variables (only allowed if configured this way) | ||
* Explicitly set through the use of a SHIM | * Explicitly set through the use of a SHIM expression <tt>session.var.set</tt>. | ||
* Imported at runtime dynamically, for example by pulling in additional user attributes from LDAP and assigning them to session variables. | * Imported at runtime dynamically, for example by pulling in additional user attributes from LDAP and assigning them to session variables. | ||
[[File:appboard-2.4-session-variables.png]] | [[File:appboard-2.4-session-variables.png]] | ||
Revision as of 10:41, 3 October 2013
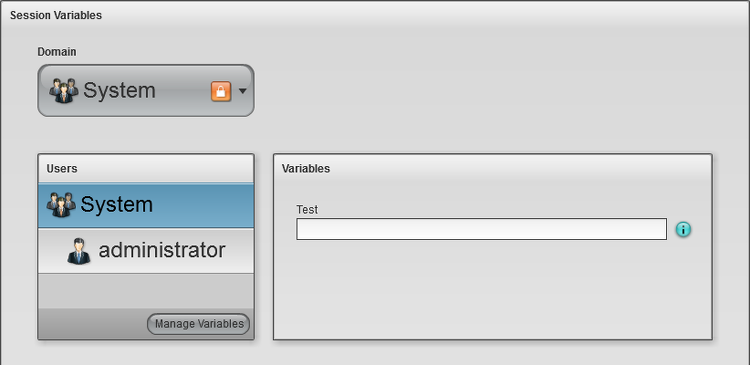
The Session Variable administration page allows the definition and default configuration for session variables within the AppBoard system.
Typical uses for session variables:
- storing environmental information that is subject to change such as database hostnames, usernames, passwords.
- associating extra information for domains and users, which can then be used for a variety of purposes such as modifying queries etc... This may be helpful in multi-tenanted deployments.
- a central place to store simple key information used in multiple places
Session variables can be used anywhere SHIM expressions are permitted using session.var.get.
There are a number of ways to set session variables:
- Session Variables administration page to define and set defaults
- URL parameters to override session variables (only allowed if configured this way)
- Explicitly set through the use of a SHIM expression session.var.set.
- Imported at runtime dynamically, for example by pulling in additional user attributes from LDAP and assigning them to session variables.