Enportal/5.6/admin/user administration/sso/kerberos: Difference between revisions
imported>Jason.nicholls |
imported>Jason.nicholls |
||
| Line 36: | Line 36: | ||
By default this file is automatically included in full system backups. | By default this file is automatically included in full system backups. | ||
=== | === Managing SSO === | ||
The steps for | The steps for managing SSO tokens at this point are the same as for the other authentication types, refer to the main [[enportal/5.6/admin/user_administration/sso|SSO documentation]] for further information. | ||
Revision as of 16:03, 21 May 2015
Overview
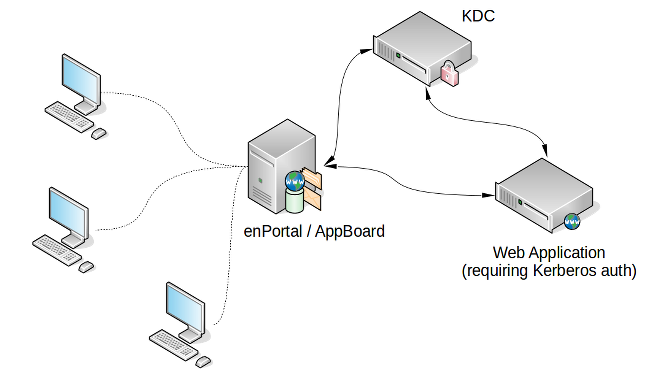
Kerberos authentication differs from basic, NTLM, and custom (application specific) authentication as enPortal also needs to communicate both with the proxied web application and the Kerberos authentication server as shown in the diagram below.
For configuration purposes managing SSO tokens is exactly the same as for the other authentication types. Kerberos does require an additional configuration file however which contains details about the authentication Domain and servers.
Configuring Kerberos
Pre-requisite
enPortal must be able to communicate with the KDC as configured in the Server Configuration below. By default this would require access from the enPortal server to the KDC on port 88.
Server Configuration: krb5.conf
For enPortal to perform Kerberos authentication it requires information about the authentication realm / domain and the actual kerberos servers to communicate with.
- Create or edit the file: [INSTALL_HOME]/server/webapps/enportal/WEB-INF/config/krb5.conf
- Use the following as a basic template and update the details to reflect the installation environment:
[libdefaults]
default_realm = AD.EXAMPLE.NET
udp_preference_limit = 1
[realms]
AD.EXAMPLE.NET = {
kdc = KDC.AD.EXAMPLE.NET
}
[domain_realms]
.ad.example.net=AD.EXAMPLE.NET
ad.example.net=AD.EXAMPLE.NET
- Restart enPortal.
By default this file is automatically included in full system backups.
Managing SSO
The steps for managing SSO tokens at this point are the same as for the other authentication types, refer to the main SSO documentation for further information.