Appboard/2.4/admin/clustering and failover
Revision as of 12:27, 21 July 2014 by imported>Jason.nicholls (→Architecture & Licensing)
Overview
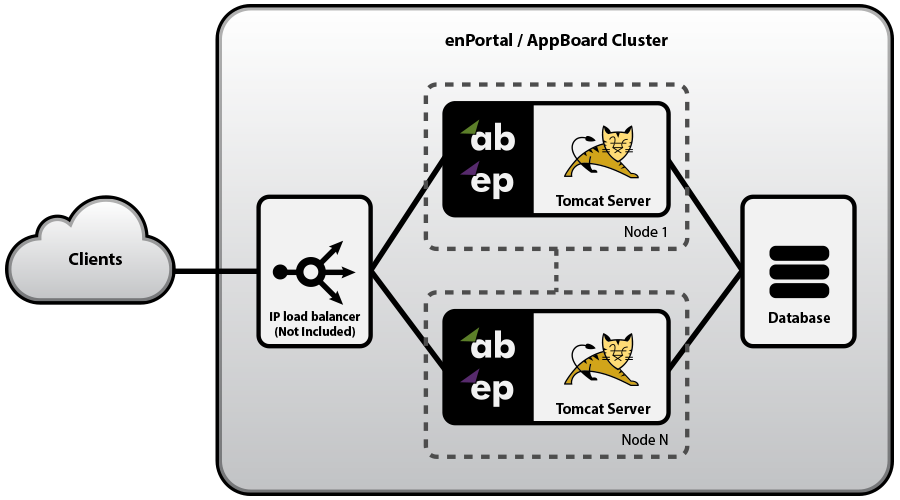
AppBoard is implemented using a highly scalable web application architecture. As a Java application running inside an Apache Tomcat server, AppBoard is able to make use of multi-core and multi-processor systems with large amounts of RAM on 64-bit operating systems. In addition to scaling vertically on a single system, AppBoard supports horizontal scaling to handle even greater loads and/or to provide for high availability environments through the use of a shared configuration database. AppBoard can be used in the following configurations:
- Load Balanced: Two or more nodes are fully operational at all times. The load balancer directs traffic to nodes based on standard load balancing techniques such as round-robin, fewest sessions, smallest load, etc... If a server is detected as down it is removed from the active pool.
- Failover: A two-node configuration with both nodes running but all traffic is routed to the primary node unless it is detected to be down. At this point the load balancer re-directs traffic to the secondary node.
- Cold Standby: A two-node configuration where the secondary node is offline in normal operation. If the primary node is detected to be down the secondary node is brought online and traffic re-directed.
Architecture & Licensing
Whether running a load-balanced, failover, or cold-standby configuration the following components are required:
- AppBoard installation per node, this includes a separate license for each node.
- External (shared) configuration database. This database is not provided by Edge and is recommended to reside on a different host to the AppBoard servers. In high availability environments the database itself should also highly available. See the System Requirements for supported external configuration databases.
- Load Balancer. This component is not provided by Edge but is required in cluster configurations.